![]() BACK TO ourHealdsburg.com
BACK TO ourHealdsburg.com
![]() BACK to NOISE page
BACK to NOISE page
Developing a new Healdsburg Noise Ordinance
![]()
Sound Level Comparison Tables
![]()
The decibel (dB) table below compares some common sounds and shows how they rank in potential harm to hearing. 70 dB is the point at which noise begins to harm hearing (EPA). To the ear, each 10 dB increase seems twice as loud.
|
Sound Levels and Human Response |
||
|
Common sounds |
Noise Level dB (A) |
Effect |
|
Rocket launching pad (no ear protection) |
180 |
Irreversible hearing loss |
|
Carrier deck jet operation Air raid siren |
140 |
Painfully loud |
|
Thunderclap |
130 |
|
|
Jet takeoff (200 ft) Auto horn (3 ft) |
120 |
Maximum vocal effort |
|
Pile driver Rock concert Home Shop Tools 65-110 dB |
110 |
Extremely loud |
|
Garbage truck Firecrackers Gas Lawn Mower at 3 feet Chain Saw 105-115 dB |
100 |
Very loud |
|
Heavy truck (50 ft) City traffic Motorcycle 80-110 dB |
90 |
Very annoying Hearing damage (8 Hrs) |
|
Alarm clock (2 ft) Hair dryer Food Blender at 3 feet Gas Lawn Mower at 100 feet |
80 |
Annoying |
|
Noisy restaurant Freeway traffic Business office Vacuum Cleaner 60-85 dB |
70 |
Telephone use difficult |
|
Air conditioning unit Conversational speech Large business office Cloths dryer 50-70dB |
60 |
Intrusive |
|
Light auto traffic (100 ft) Dishwasher in next room |
50 |
Quiet |
|
Living room Bedroom at night Quiet office Bird calls - 44 dB |
40 |
|
|
Library Soft whisper (15 ft) Quiet Rural nighttime |
30 |
Very quiet |
|
Broadcasting studio |
20 |
|
|
|
10 |
Just audible |
|
|
0 |
Hearing begins |
| Construction Equipment | ||
| Front-end Loader |
85 |
|
|
Dozer |
80 | |
| Jackhammer | 88 | |
|
Saw (concrete cutting) |
83 | |
|
Semi Dump Truck |
80 | |
| Concrete truck/mixer | 85 | |
|
Generator |
78 | |
|
Air Compressor |
81 | |
![]()
Typical Outdoor Sound Measured on a Quiet Suburban Street (EPA)
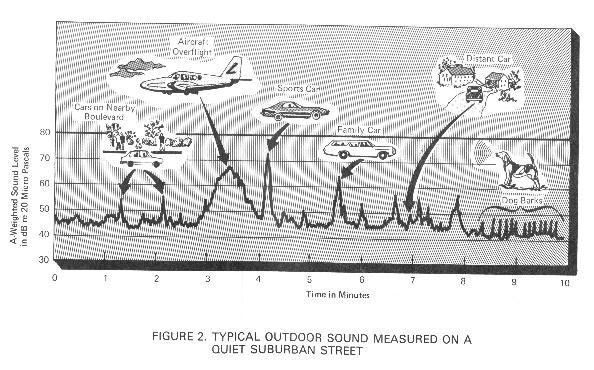
Figure 2, from an EPA report, "Information on Levels of Environmental Noise Requisite to Protect Public Health and Welfare with an Adequate Margin of Safety," (EPA/ONAC 550/9-74-004, March, 1974). shows a ten-minute time history of outdoor sound measured on a front lawn at a quiet suburban location on a typical, otherwise uneventful, afternoon. The maximum sound level, 73 dB(A), occurs instantaneously when a sports car passes on the nearby street. Often, the "noise floor" or background sound of an area is expressed as the sound level exceeded 90 percent of the time, symbolized as the L90. In Figure 2, the L90 is approximately 44 dB(A); that is, the ambient sound level exceeds 44 dB(A) for about 90 percent of the time interval depicted. In other words, the background sound level is about as quiet as it gets at a particular location. The one percentile sound level, L1, is generally taken to be representative of typically intrusive, high sound levels observed during a time interval. (one percent of the 10 minute interval in Figure 2 is six seconds).
![]()

1971 EPA study
Generalized Individual Daily Noise Exposure Patterns (EPA)
These sound levels represent sounds that are averaged for each hour to obtain a noise exposure level. This chart is developed by EPA from a very small sample in 1974. For example for "household sound levels" only 12 houses were monitored to establish this EPA chart.
The current Healdsburg Noise Regulations allow daytime noise as high as 86 dB in Residential Areas.
![]()
![]()
![]() BACK TO ourHealdsburg.com
BACK TO ourHealdsburg.com
![]() BACK to NOISE page
BACK to NOISE page
webmaster:
![]() thomasjoad@ourHealdsburg.com
thomasjoad@ourHealdsburg.com
© 2002 ourHealdsburg.com™. All rights reserved.