 |
|||||||
 |
Renewable Energy
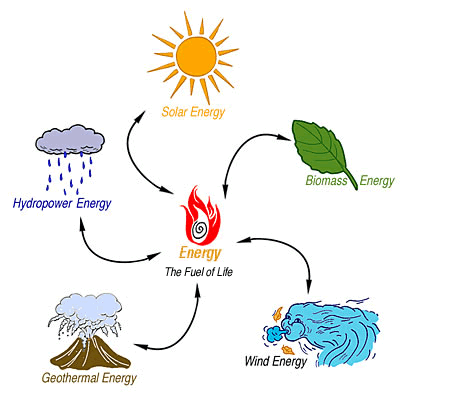 Renewable energy's impact on the world's energy picture is significant. Many important events have occurred during the history of using renewable sources to generate electricity - but the overall use of these fuels has declined by about 17 percent from their 1996 peak to about 6 quads in 2003. The use of renewable energy is not new. Five generations (125 years) ago, wood supplied up to 90 percent of our energy needs. Due to the convenience and low prices of fossil fuels, wood use has fallen. Now, the biomass which would normally present a disposal problem is converted into electricity (e.g., manufacturing wastes, rice hulls, and black liquor from paper production). Historically, low fossil fuel prices, especially for natural gas, have made growth difficult for renewable fuels. The deregulation and restructuring of the electric power industry could have a major impact on renewable energy consumption. Demands for cheaper power in the short term would likely decrease demand for renewable energy, while preferences for renewables included in some versions of proposed electricity restructuring legislation would breathe new life into this industry. Use of renewables in the United States is not currently expected to approach that of the major fuels, and due to their limitations (e.g., their intermittent nature - cloudy days have no solar gain, quiet days mean no wind blows to drive wind turbines, dams are primarily for flood control, so hydroelectricity production varies as dams' water levels change), renewables may never provide "the" answer to all energy problems. Around the world, renewable energy is proving to be of great value. In 2003, about 6.2 Quadrillion Btu (Quads) of US energy came from renewable fuels. Each of the energy sources we use is measured, purchased, and sold in a different form. Many units of measurement are used to measure the energy we use each day. Learn more about converting energy units in the Units of Measurement section. Last Revised: January 2004 Sources: Energy Information Administration, Energy INFOcard, October 2004.
Biodiesel -- a Renewable Fuel
BIODIESEL MADE FROM VEGETABLE OILS AND ANIMAL FATSBiodiesel is a renewable fuel that can be used instead of diesel fuel made from petroleum. Biodiesel can be made from vegetable oils, animal fats, or greases. Most biodiesel today is made from soybean oil. About half of biodiesel producers are able to make biodiesel from used oils or fats, including recycled restaurant grease. Biodiesel is most often blended with petroleum diesel in ratios of 2 percent (B2), 5 percent (B5), or 20 percent (B20). It can also be used as pure biodiesel (B100). Biodiesel fuels can be used in regular diesel vehicles without making any changes to the engines. It can also be stored and transported using diesel tanks and equipment. Fueling engines with biodiesel has just started to catch on, but this isn't a new idea. Before petroleum diesel fuel became popular, Rudolf Diesel, the designer of the diesel engine, experimented with using vegetable oil (biodiesel) as fuel. BIODIESEL AS A TRANSPORTATION FUELMost trucks, buses, and tractors in the United States use diesel fuel. Diesel is a nonrenewable fuel made from petroleum. Using biodiesel means that we use a little bit less petroleum. Biodiesel results in less pollution than petroleum diesel. Any vehicle that operates on diesel fuel can switch to biodiesel without changes to its engine. Because it is so clean burning and easy to use, biodiesel is the fastest growing and most cost efficient fuel for fleet vehicles. Many school districts are switching to biodiesel blends for their school buses. Biodiesel is also being used for fleets of snowplows, garbage trucks, mail trucks, and military vehicles. So far, the use of biodiesel has been limited to fleets of vehicles that have their owner fueling stations. As the number of public fueling stations that offer biodiesel grows, it may become more popular with individual consumers. B100 and biodiesel blends are sensitive to cold weather and may require special anti-freeze, just like petroleum-based diesel fuel does. Biodiesel acts like a detergent additive, loosening and dissolving sediments in storage tanks. Because biodiesel is a solvent, B100 may cause rubber and other components to fail in older vehicles. This problem does not occur with biodiesel blends. BIODIESEL AND THE ENVIRONMENTBiodiesel is renewable, nontoxic, and biodegradable. Compared to diesel, biodiesel, is significantly cleaner burning. It produces fewer air pollutants, like particulates, carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and air toxics. It does slightly increase emissions of nitrogen oxides, though. Biodiesel produces less black smoke, and smells better, too. Sometimes biodiesel smells like french fries! Regular diesel fuel contains sulfur. Sulfur can cause damage to the environment when it is burned in fuels. New environmental laws will require the amount of sulfur in diesel fuel to be dramatically reduced over the next few years. When sulfur is removed from regular diesel fuel, the fuel doesn't work as well. Adding a small amount of biodiesel can fix the problem. Biodiesel has no sulfur, so it can reduce sulfur levels in the nation's diesel fuel supply while making engines run more smoothly. Acknowledgments: The information for the Bio-Kids sections of this web site have been graciously loaned to Envira Fuels by the Department of Energy's - Energy Information Administrations: Energy Kid's Page at: http://www.eia.doe.gov/kids/energyfacts/sources/renewable/biodiesel.html
|
||||||
|
|||||||